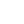The Pythagorean Theorem
Pythagorean Theorem: In a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse c is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the legs a and b.
If two measures of the sides of a right triangle are known, the Pythagorean Theorem can be used to find the measure of the third side.
Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem: If c is the measure of the longest side of a triangle, a and b are the lengths of the other two sides, and c² = a² + b² , then the triangle is a right triangle.
If a triangle has sides of lengths a, b, and c where c is the longest length and c2 = a2 + b2, then the triangle is a right triangle with c its hypotenuse.
If a, b, and c represent the lengths of the sides of a triangle, and c is the longest length, then the triangle is obtuse if c2 > a2 + b2, and the triangle is acute if c2 < a2 + b2.
Find out more about the Pythagorean Theorem by reading the explanation below.
Practice: Use the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse in answering the exercises.