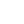The Pythagorean Theorem and Its Converse
The two sides that form the right angle are called the legs. In the triangle above, the lengths of the legs are 3 units and 4 units. The side opposite the right angle is called the hypotenuse.
Pythagorean Theorem: In a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse, c, is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the legs, a and b.
A converse of a theorem is the reverse, or opposite, of the theorem. You can use the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem to test whether a triangle is a right triangle.
Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem: If c is the measure of the longest side of a triangle and c² = a² + b², then the triangle is a right triangle.
Read the explanation below to learn more about the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse.
The Pythagorean Theorem and Its Converse
Practice: Answer the following exercises by using the Pythagorean Theorem to solve problems.